CHEMICAL FERTILIZER (PHOSPHATE / POTASH FERTILIZER PROCESSING)
China leading manufacturer of chemical fertilizer machines, EMCC design high quality, efficiency, and longevity Urea/DAP/MAP/TSP/MKP/DKP/Phosphorus Fertilizer equipments for compound fertilizer plants with best price.
THE MAIN TYPES OF FERTILIZERS INCLUDE THE FOLLOWING
Nitrogen fertilizers: Nitrogen fertilizers provide plants with the essential nitrogen element, promoting leaf growth and chlorophyll synthesis. Common nitrogen fertilizers include urea, ammonium fertilizers such as ammonium sulfate and ammonium nitrate.
Phosphorus fertilizers: Phosphorus fertilizers provide plants with the essential phosphorus element, promoting root development, floral bud differentiation, and fruit maturation. Common phosphorus fertilizers include diammonium phosphate (DAP), triple superphosphate (TSP), monopotassium phosphate (MKP), among others.
Potassium fertilizers: Potassium fertilizers provide plants with the essential potassium element, promoting root development, stress resistance, and fruit quality. Common potassium fertilizers include potassium chloride, potassium sulfate, among others.
Compound fertilizers: Compound fertilizers contain multiple nutrients and can provide nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, and other essential elements simultaneously. Common compound fertilizers include NPK compound fertilizers, available in granular or liquid form.
In addition to these main types of fertilizers, there are also trace element fertilizers such as boron fertilizers, zinc fertilizers, etc., which provide plants with essential micronutrients.
These fertilizers play a vital role in agricultural production by supplying plants with necessary nutrients, promoting growth, and improving crop yield and quality. The choice of fertilizer depends on soil analysis and crop requirements.
THE FOLLOWING COMMONLY USED FERTILIZERS REQUIRE PELLETIZATION
Monoammonium phosphate (MAP), diammonium phosphate (DAP), and triple superphosphate (TSP): DAP and TSP are common phosphorus fertilizers that contain phosphorus and nitrogen elements. Due to their hygroscopic and highly soluble nature, pelletization helps prevent caking and improves their storage stability.
Monopotassium phosphate (MKP) and dipotassium phosphate (DKP): MKP and DKP are common potassium-phosphorus fertilizers that contain phosphorus and potassium elements. Pelletization improves their flowability and ease of application, while also preventing caking and enhancing storage stability.
Potassium fertilizers: such as potassium chloride and potassium sulfate, can undergo pelletization to improve their physical properties, making them easier to store, transport, and apply.
Compound fertilizers: Compound fertilizers typically contain multiple nutrients, such as NPK compound fertilizers. Pelletization allows for uniform mixing of these components and formation of granules, improving convenience and stability during application.
By pelletizing these fertilizers, their physical properties are enhanced, making them easier to store, transport, and apply. Pelletized fertilizers exhibit better flowability, uniformity, and stability, thereby improving fertilization efficiency and the absorption and utilization rate by crops.
GRANULATION METHODS FOR DIFFERENT FERTILIZERS
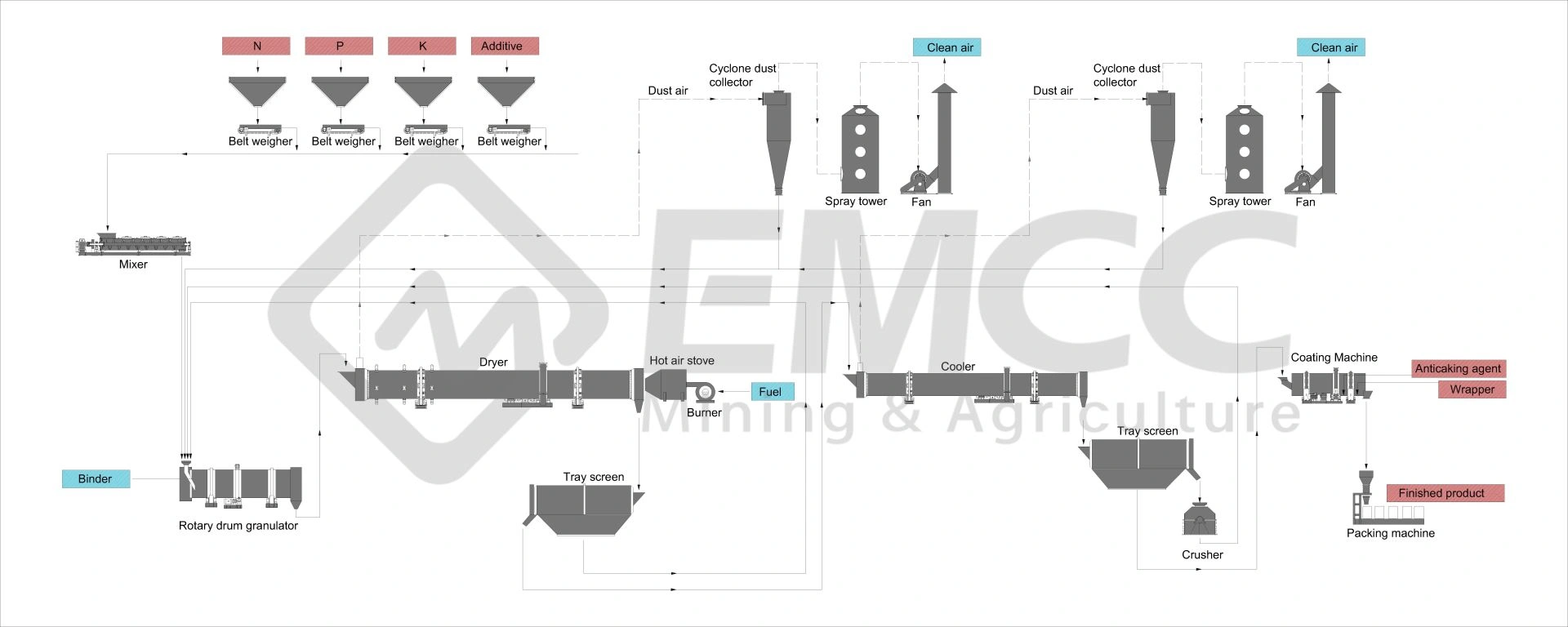
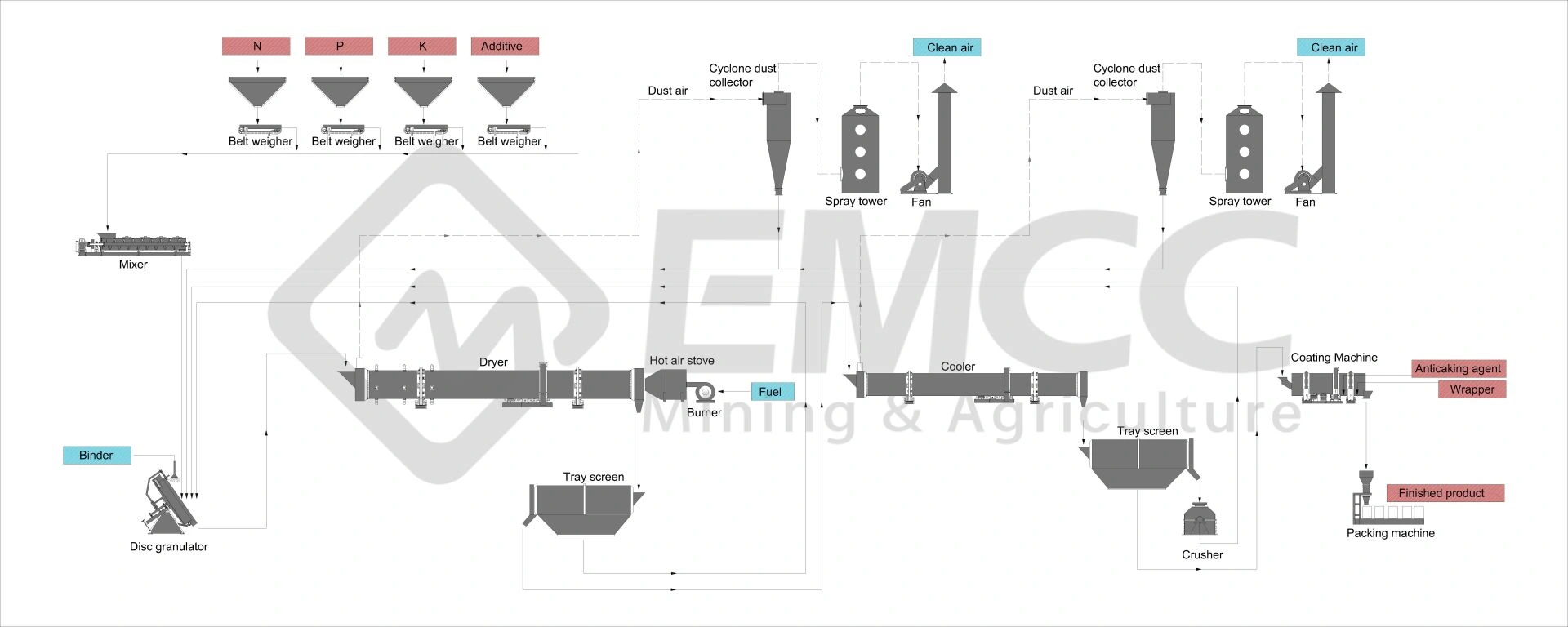
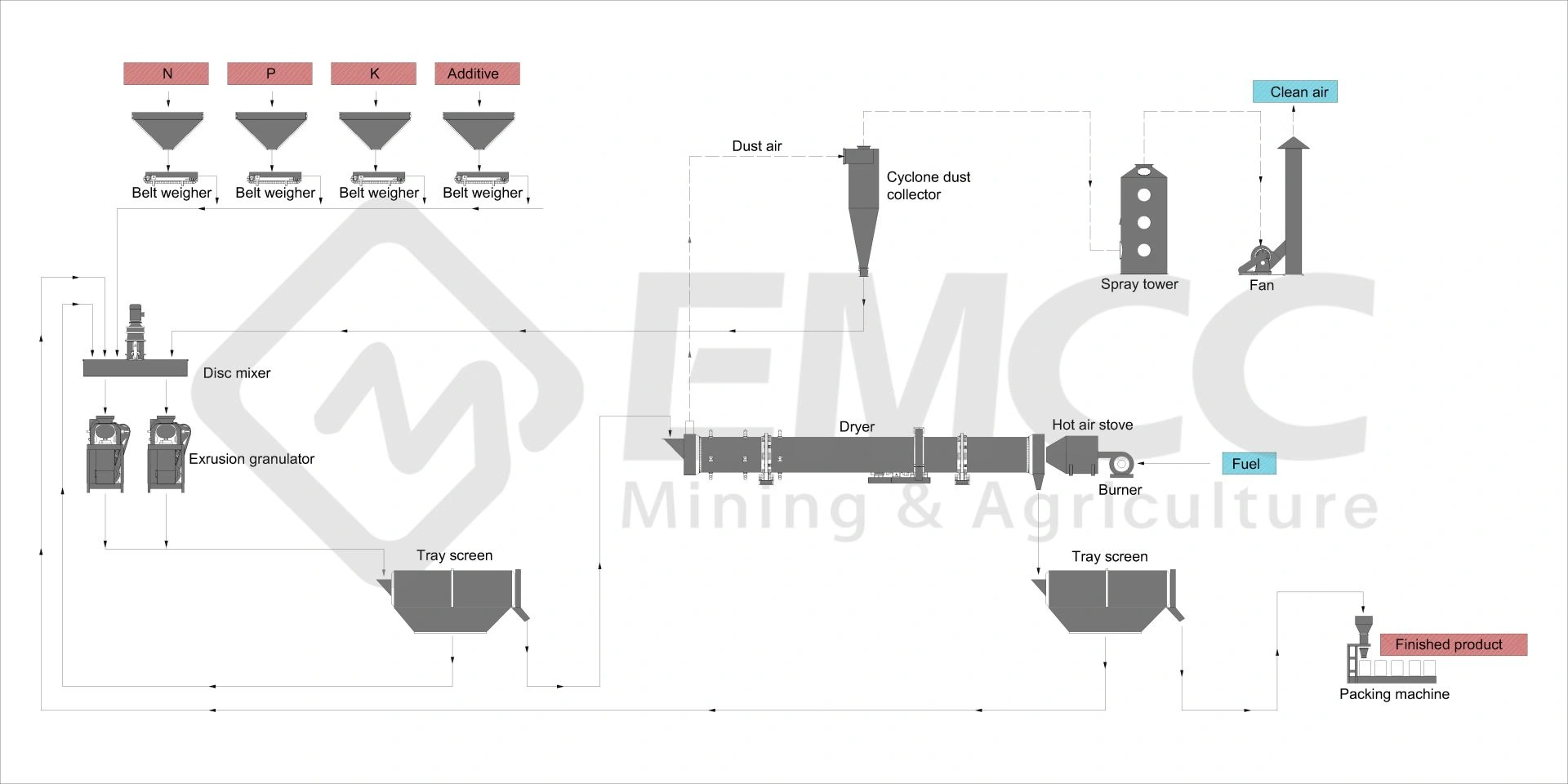
Phosphoric acid monoammonium (MAP), diammonium phosphate (DAP), ammonium phosphate sulfate (TSP), and compound fertilizers are generally pelletized using wet granulation methods such as rotary drum granulation production lines and disc granulation production lines.
On the other hand, potassium chloride and potassium sulfate are typically pelletized using Pressure granulation methods.
RESOURCES
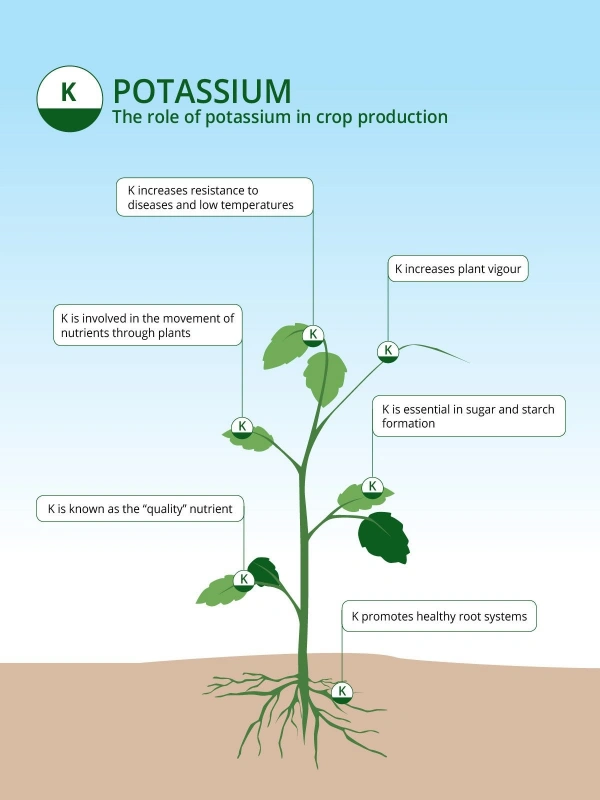
Potassium Based Fertilizers
Potassium (K) is one of the three essential plant macronutrients,

Phosphorus Fertilizers
In the quest for sustainable agriculture, phosphorus fertilizers stand at