Liquid Fertilizer
China leading manufacturer of liquid fertilzer production line, EMCC design high-quality and low energy consumption liquid fertilizer making line for fertilizer plants with low price and cost.
LIQUID FERTILIZER
Liquid fertilizer is a form of fertilizer that can be directly applied or sprayed with water as a carrier. It includes various water-soluble fertilizers such as liquid nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, and compound liquid fertilizers. The advantages of this type of fertilizer are easy application, high absorption efficiency, and the ability to be directly sprayed on plant leaves or applied through irrigation systems. China EMCC have the complete liquid fertilzer production line for our clients.
THE PRODUCTION PROCESS OF LIQUID FERTILIZER TYPICALLY INVOLVES THE FOLLOWING STEPS:
Raw material selection: Choose inorganic or organic fertilizers that contain necessary nutrients (such as nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, etc.) as raw materials.
Formulation: Mix the required nutrient elements together according to the fertilizer formula and crop requirements to form a nutrient solution.
Dissolution: Dissolve the mixed fertilizer in water to form liquid fertilizer.
Screening and filtration: Screen and filter the dissolved liquid fertilizer to remove large particles and insoluble substances.
Stabilization treatment: To prevent nutrient elements from precipitating or layering during storage and use, stabilization treatment may be necessary.
Packaging and storage: Finally, package and store the produced liquid fertilizer for transportation and sale.
WHEN SELECTING RAW MATERIALS FOR LIQUID FERTILIZER, THE FOLLOWING FACTORS NEED TO BE CONSIDERED:
Nutrient content: The selected raw materials should have sufficient nutrient content to meet the nutritional needs of crops. For example, you may need to choose raw materials with high concentrations of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium.
Solubility: The raw materials need to dissolve well in water to form liquid fertilizer. Insoluble substances may hinder the effectiveness of the fertilizer or cause clogging in the fertilization equipment.
Stability: The raw materials should have good stability after dissolution, without precipitation or layering during storage and use.
Safety: The raw materials should be safe and not have harmful effects on humans, crops, and the environment.
Cost: Cost considerations are also important when selecting raw materials to ensure that the production cost and selling price of liquid fertilizer can achieve economic benefits.Common raw materials for liquid fertilizers include inorganic salts such as urea, potassium nitrate, ammonium nitrate, potassium dihydrogen phosphate, phosphoric acid, and potassium sulfate, as well as organic substances such as humic acid, amino acids, and protein hydrolysates. These raw materials have good solubility and nutrient content and can be selected and blended according to specific needs.
When applying liquid fertilizer, the appropriate application rate and timing can be selected based on the crop’s requirements and soil conditions to achieve optimal fertilization efficiency. By using liquid fertilizer, crop nutrients can be quickly replenished, leading to increased yield and quality while reducing environmental impact.
RESOURCES
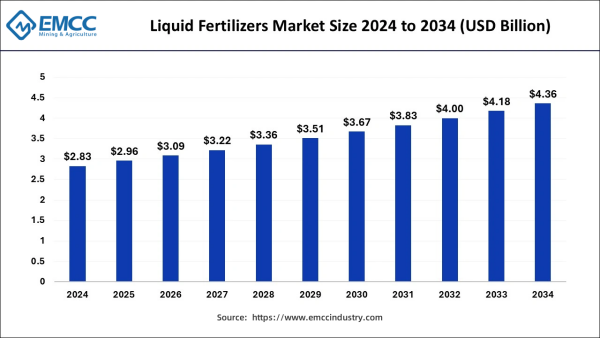
Liquid Fertilizers Market Size, Share, and Trends 2025 to 2034
The global liquid fertilizers market size is estimated at USD

Pros and Cons of Granular and Liquid Fertilizers
Theoretically, plants can’t tell the difference between nutrients supplied by
